What you'll learn:
- What is an AMR sensor?
- How does an AMR sensor perform measurements for rotating elements?
- 进行电和机械角度测量。
The position of moving and rotating elements can be measured in many different ways. Apart from optical encoders, Hall sensors, and resolvers, magnetic sensors based on the magnetoresistive effect are used. There are giant magnetoresistive (GMR) and tunnel magnetoresistive (TMR) effects as well as an anisotropic magnetoresistive (AMR) effect, which this article delves into further.
TheADA4570AMR sensor developed byAnalogDevices(ADI)makes use of the characteristic of ferromagnetic materials whereby the electrical resistance depends on the direction of magnetization. This phenomenon was discovered by William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) around 1851:
R = R0 + ΔR × cos(2 × α) (1)
where α is the angle between the direction of magnetization and the direction of current flow.
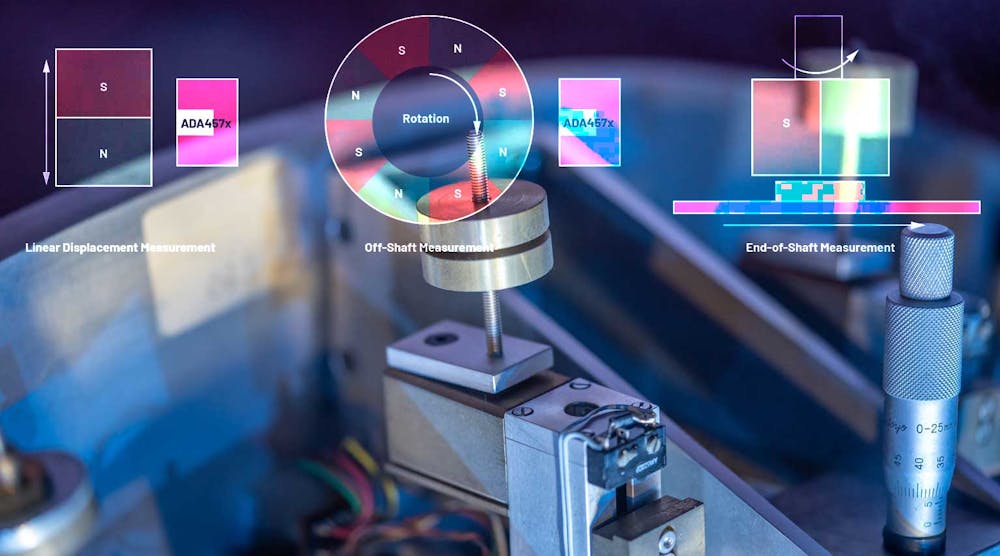
For an optimal sensor response in linear displacement measurements, the sensor is placed such that the magnet and sensor are in the same plane and the center of the magnet is in line with the center of the sensor. Because an AMR sensor can’t distinguish between north and south poles, the position of the magnet can’t be changed.
Measuring Rotating Elements
对于旋转元素,所谓的输出轴或结束of-shaft configurations are common. In the example with the off-shaft configuration(Fig. 1), the sensor sine/cosine outputs repeat the absolute information for every pole—for example, 45 degrees for a 4-pole pair magnet.
In the end-of-shaft configuration(Fig. 1, again), the sensor is situated below a rotating dipole magnet; here, the north and south poles form a uniform field above the center of the magnet. The sensor is positioned in such a way that the magnetic field and the element to be measured are in the same plane. A typical application is rotor position measurement and control in brushless dc motors.
对于特征在于180度角传感器的AMR传感器,电动机必须是均匀的杆配对运动器。具有奇数杆对的电动机需要360度信息以进行换向。与也用于电动机控制中的常规大厅传感器相比,AMR传感器(例如ADA4570)和ADA4571have a higher precision. They also reduce the torque ripple and provide true power on absolute position information after startup or an idle state irrespective of the motor position.
Closer Look at AMR Tech
ADI’s AMR technology measures the angle by means of two Wheatstone bridges; one rotated by 45 degrees with respect to the other(Fig. 2).
该角度是通过正弦和余弦函数计算的,代表与传感器相关的0至180度的方向(ADA4570):
α = arctan2 (VSIN/VCOS)/2(2)
In AMR sensors, differentiation is made between electrical angles and mechanical angles. Due to the working principle of AMR sensors and the above-described 45-degree angle between the Wheatstone bridges, the absolute angle can be measured by means of Equation 2 over 180-degree mechanical rotation. The electrical period repeats twice over the 360-degree rotation for a dipole magnet.
Given that AMR sensors work in saturation, the absolute field strength is irrelevant, with a certain minimum magnetic-field strength present allowing for robust systems when working with strong magnets.
除了光学传感器,霍尔传感器和解析器外,磁性传感器还提供了一种优雅的解决方案,可在许多不同的应用中以高精度和鲁棒性测量位置。ADI为此任务提供了许多可能性,例如ADA4570,ADA4571和ADA4571-2需要冗余的地方。要了解有关此主题的更多信息,请参见下面列出的引用。
参考
盖尔,罗伯特。“AN-1314ApplicationNote:AMRAngleSensors.” Analog Devices, Inc., October 2014.
Nicholl, Enda. “DualAMRMotorPositionSensor为了安全Critical申请.”模拟对话, Vol. 53, No. 4, November 2019.














.jpg?auto=format,compress&fit=crop&h=139&w=250&q=45)

