您将学到什么:
- 由于COVID-19的大流行,测量室内空气质量至关重要。
- 现有公司2市场上的传感器解决方案具有明显的限制,可能会损害性能。
- MEMS技术实施的光声光谱的进步克服了当前的许多CO2drawbacks.
自COVID-19大流行开始以来,科学家对病毒的主要传播途径有了更好的了解。研究表明,该疾病主要是通过从一个人到另一个人的紧密接触,通常是在狭窄的室内空间中传播。这是一个重要的考虑因素,因为美国环境保护署(EPA)的统计数据表明,人们在室内的时间占90%,在那里他们可能会处于最高风险。
因此,对室内空气质量的有效监控比以往任何时候都变得更加关键。空气质量最可靠的测量指标之一是CO2浓度。如果房间通风严重,则可以2concentration level starts to rise. As an example, in a poorly ventilated room measuring roughly 4 m2containing a single individual, the CO2value could go from 500 ppm (0.05%) to at least 1,000 ppm (0.1%) within 45 minutes.
因为合作2是无色和无味的气体,没有视觉或嗅觉表明其浓度已经增加。但是,在较高的水平下,它可能开始引起不舒服的身体症状,例如头痛和嗜睡。从2,000 ppm开始(0.2%),人类的认知能力可能会受到损害,并且在较高水平上对健康有严重的危险。
关于COVID-19,室内CO2concentration becomes a critical factor. As people exhale more CO2in the air, they produce a high number of aerosols—tiny respiratory droplets or particles that can spread across a room. Numerous research papers show that aerosols linger for extended periods in poorly ventilated rooms, increasing the risk of long-range airborne transmission of the virus.
A study conducted by TU Berlin revealed that indoor climates play a significant role in health outcomes, as pathogens can be suspended in the air inside poorly ventilated rooms for long periods of time. As such, a frequent supply of fresh air is recommended as a means of reducing the chance of infection.
现有CO的缺点2传感器
有了了解很多空气的CO2可以充当19号传输风险,对CO的使用越来越兴趣2measuring solutions across a broad range of indoor locations, including gyms, bars, and restaurants. Yet while demand for gas-sensing technology is on the rise, some existing CO2传感器解决方案具有明显的局限性,可能会损害性能。
For example, non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) CO2传感器包含大量内部组件,例如IR光源,样品室,光谱滤波器以及参考和吸收IR检测器。最终的传感器相对庞大且昂贵。
较小且较便宜的替代方案是估计的CO2(ECO2) 传感器。这些设备使用算法来计算等效CO2来自已知的总挥发性有机化合物浓度的值。该估计是在一组假设而不是实际测量值上提出的,因此该解决方案具有自己的缺点。因此,搜索继续寻找紧凑且具有成本效益的传感器,该传感器提供准确而真实的CO2测量。
光声学光谱的进步
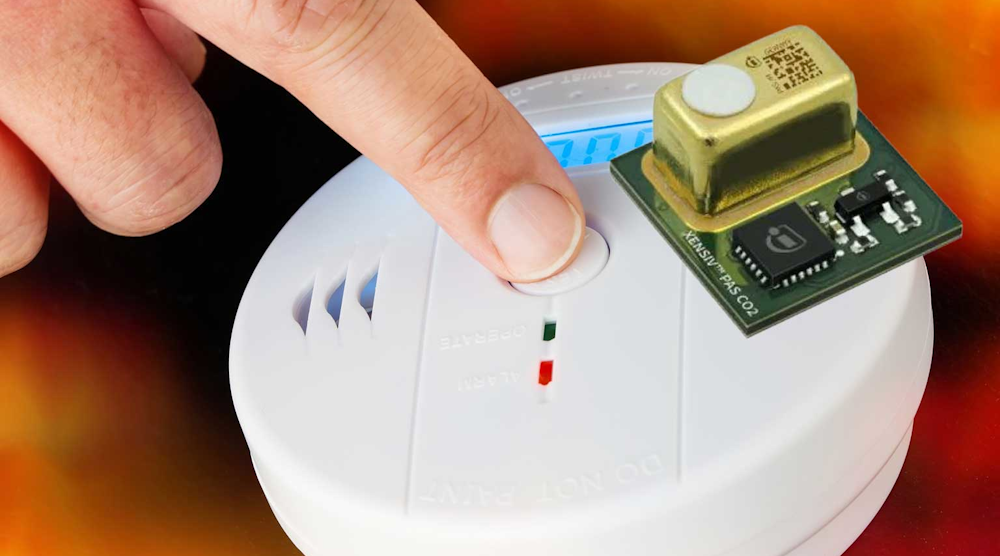
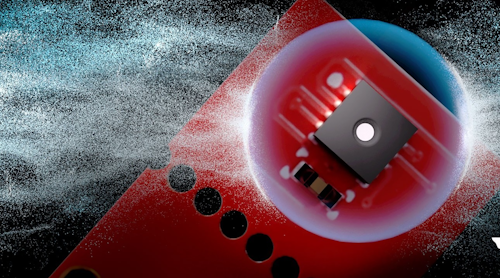
利用其微电机械系统(MEMS)技术,Infineon开发了一个新公司2基于光声光谱(PAS)的传感器克服了许多缺点,使得CO2传感技术适合各种应用程序(图。1)。该技术基于以下原理:气体分子仅吸收具有特定波长的光。
1.光声光谱(PAS)原理是基于戒律:气体分子仅吸收具有特定波长的光。对于CO2,波长为4.2 µm。
对于CO2,波长为4.2 µm。In terms of the detection process, light at this wavelength, generated via a pulsing infrared source with an optical filter, is passed through a sample of ambient air. This causes rapid heating and cooling, and thus thermal expansion and contraction of the target gas. It results in a pressure change that can be accurately recorded using an acoustic detector which is optimized for low frequencies. This signal is then analyzed to provide insight into the amount of CO2in the air—the stronger the signal, the higher the CO2浓度。
充当压力传感器的高度敏感的MEMS麦克风用于检测气体,从而在微型化方面具有优势。传感器的其他元素是光声传感器,红外源和光学滤波器。微控制器处理信号处理和MOSFET为红外源提供动力。
Infineon克服了重大挑战,以将检测器的性能提高到极限,并将系统噪声降低到绝对最小值。MEMS检测器通过封装与外部噪声分离出声学。仅源自CO的压力变化2检测到腔室中的分子。所有组件,包括孤立的气体检测室和相关电子设备,都集成在PCB上。吸收室与外部噪声进行声学分离,以确保准确的CO2sensing data. Otherwise, the function of CO2detection would be significantly impaired.
According to Infineon, itsXensiv PAS CO2传感器是该行业的第一个Real Co2基于PAS原理的传感器(图2)。传感器受益于超敏感的mems麦克风,该麦克风可以检测CO所产生的压力变化2传感器腔内的分子而无需捡起外部噪声。作为输出,它可以交付CO2集中度为百万。
2. Xensiv Pas CO2是真实的CO2由唯一的PAS检测原理启用了前所未有的小型尺寸的传感器。
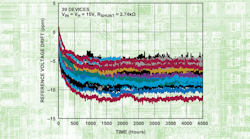
性能数据证实了高质量的结果s even with the smallest pressure fluctuations. As a result, only the smallest amounts of gas are required for an ultra-precise determination, meaning the dimensions of the sample chamber could be made as small as possible.
Xensiv PAS CO2传感器的四倍(14×13.8×7.5毫米)小于典型的NDIR传感器,仅在两克时轻至三倍,可在系统设计中节省超过75%的空间。
co2COVID-19管理传感器
Xensiv Pas CO2显示出帮助减轻Covid-19的传播的潜力。随着世界试图平衡控制疾病传播并重新开放关键基础设施的需求,传感技术将成为有效监测空气质量和减少室内环境中气溶胶的越来越重要的工具。
Even before the pandemic began, the Federal Environment Agency of Germany and the American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and Air Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) had published recommendations stating that the CO2concentration should not exceed 1,000 ppm in classrooms and offices—as opposed to 400 ppm in open, fresh air.
了解很多含有CO的空气2在房间里有高度集中的地方,都可以呼出,CO的安装2衡量技术可能会扩展到与多个人的室内环境。廉价和紧凑的公司2measuring devices promise to broaden the number of sites that could adopt sensor technologies to warn against high concentrations of CO2在空气中以及相应高水平的气溶胶中,提供了一种更容易获得的减轻病毒传播的方法。
在室内环境中,如何在实践中使用此类设备?一种解决方案可能是CO的发展2感知交通电灯系统。在此应用程序中,传感器网络可以连接到用于数据智能和远程访问的云解决方案,并用于警告High Co的占用者2和气溶胶水平。交通灯系统可以发出明确的信号,以更好地为建筑物中的单个房间或特定区域提供通风。
A Broad Range of Applications
In addition to controlling the risk of infection, data measured by CO2传感器可以馈入控制通风的智能建筑自动化系统,称为需求控制通风(DCV)。在这样的系统中2measurements could be used for real-time adjustment of air mixtures in a room, automatically matching it to that of the air outside. This ensures that indoor CO2集中度仍然处于可接受的水平,从而在舒适和福祉方面提供了重大的好处。
办公室和房屋中有效的空气管制也可以节省大量能源,同时降低了相关成本和CO2emissions.估计表明在美国各地的建筑物中使用DCV可以将总功耗减少多达五分之一,每年节省约800亿美元的能源成本。
例如,美国平均大约7,000平方米的学校年度HVAC能源消耗约为5.6 usd/m²。基于DCV的能源效率提高了20%,基于80,000 kWh的节省(假设10美分/千瓦时),节省的价格将相当于每年约8,000美元,这转化为35吨2减少排放。
Small CO2传感器还适用于诸如智能助手在连接房屋和基于物联网的设备中的应用,例如空气净化器和恒温器,婴儿监视器,甚至智能照明。将来可能会遵循其他申请,特别是在农业中,2传感器可用于促进智能的温室和室内/垂直农业。他们还可以支持城市管理/公司2排放控制政策正在安装在大批人经常聚集的公共汽车站之类的地方。
高准确公司2sensing in a compact system design, such as the XENSIV PAS CO2, opens the door to solutions for energy savings and compliance with major smart building standards. Moreover, with the specter of COVID-19 and other airborne infectious diseases, the increasing deployment of such technology provides a powerful tool for public health.