This article is part of theAnalogSeries:Back to Basics: Impedance Matching
Download this article in .PDF format
The L-network is a real workhorse impedance-matching circuit(see “Back to Basics: Impedance Matching (Part 2)” )。虽然它适合许多应用程序,一个更复杂的circuit will provide better performance or better meet desired specifications in some instances. The T-networks and p-networks described here will often provide the needed improvement while still matching the load to the source.
Rationale For Use
The main reason to employ a T-network or p-network is to get control of the circuit Q. In designing an L-network, the Q is a function of the input and output impedances. You end up with a fixed Q that may or may not meet your design specs. In most cases the Q is very low (<10). This may be too low for applications where you need to limit the bandwidth to reduce harmonics or help filter out adjacent signals without the use of additional filters. Remember the relationship for determining Q:
Q = f/BW
where f is the operating frequency and BW is the bandwidth.
The T-networks and p-networks provide enough variety to fit almost any situation.
p-Networks
基本p-network的主要应用是马tch a high impedance source to lower value to load impedance. It can also be used in reverse to match a low impedance to a higher impedance. The low pass version inFigure 1ais the most common configuration, though the high pass version inFigure 1balso can be used.
You may design a p-network using L-network procedures. The p-network can be considered as two L-networks back to back. To use the L-network procedures, you need to assume an intermediate virtual load/source resistance RVas shown inFigure 1c。You can estimate RV来自:
RV= RH/(Q2+ 1)
RH两个des的更高吗ign impedances Rgand RL。The resulting RVwill be lower than either Rgor RLdepending on the desired Q. Typical Q values are usually in the 5 to 20 range. An example will illustrate the process.
p-Network Design Example
Assume you want to match a 1000-Ω source to a 100-Ω load at frequency (f) of 50 MHz. You desire a bandwidth (BW) of 6 MHz. The Q must be:
Q = f/BW = 50/6 = 8.33
RV= RH/(Q2+ 1) = 1000/[(8.33)2+ 1] = 1000/70.4 = 14.2 Ω
The design procedure for the first L-section uses the formulas from“Back to Basics: Impedance Matching (Part 2).”Use the desired Q of 8.33 with an RLvalue equal to RV。
The inductor L1 value is:
XL= QRL= 8.333(14.2) = 118.3 Ω
L = XL/2pf
L1= 118.3/2(3.14)(50 x 106)
L1= 376.7 nH
The capacitor C1value is:
XC1= Rg/ Q
XC1= 1000/8.33 = 120 Ω
C1= 1/2pfXC
C1= 1/2(3.14)(50 x 106)(120)
C1= 26.54 pF
Now calculate the second section with L2and C2using an Rgvalue of RVor 14.2 Ω with the load RLof 100 Ω . The Q is now defined by the L-network relationship:
Q = √(RL/ Rg) – 1
Rgin this case is RVor 14.2 Ω.
Q = √(100/14.2) – 1 = √(7) – 1 = √6 = 2.46
The inductance L2, then, is:
XL2= QRg= 2.46(14.2) = 35 Ω
L2= XL/2pf
L2= 35/[2(3.14)(50 x 106)]
L2= 111.25 nH
The capacitance C2is:
XC2= RL/ Q
XC= 100/2.46 = 40.65 Ω
C2= 1/2pfXC
C2= 1/[2(3.14)(50 x 106)(40.65)]
C2= 78.34 pF
Note that the two inductances are in series so the total is just the sum of the two or:
L1+ L2= 376.7 + 111.25 = 487.97 nH
Figure 2shows the final circuit.
This Web tool provides the same results:
http://bwrc.eecs.berkeley.edu/research/rf/projects/60ghz/matching/impmatch.html%20
T-Networks And LCC Design Example
Figure 3illustrates the basic T-networks. The basic T shown inFigure 3ais not widely used, but its variation inFigure 3bis. The second network is called an LCC network.
To design these networks, you can also consider them as two cascaded L-networks. However, since the version inFigure 3bis so common, you can also use some shortcut formulas. Here is the procedure:
1. Select the desired bandwidth and calculate Q.
2. Calculate XL= QRg
3. Calculate XC2= RLv[Rg(Q2+ 1)/RL– 1]
4. Calculate XC1= Rg(Q2+ 1) / (QR问L/(QRL– XC2)]
5. Calculate the inductance L= XL/2pf
6. Calculate the capacitances C = 1/2pfXC
Assume a source or generator resistance of 10 Ω and a load resistance of 50 Ω . Let Q be 10 and the operating frequency be 315 MHz.
XL= QRg= 10(10) = 100 Ω
L = XL/2pf = 100/2(3.14)(315 x 106) = 50 nH
XC2= RLv[Rg(Q2+ 1)/RL– 1] = 50v{[10(101)/50] – 1} = 219 Ω
XC1= Rg(Q2+ 1)/Q [QRL/(QRL– XC2)] = 10(101)/10[500/(500 – 219)] = 179 Ω
C2= 1/2pfXC= 1/2(3.14)(315 x 106)(219) = 2.31 pF
C1= 1/2pfXC= 1/2(3.14)(315 x 106)(179) = 2.82 pF
Applications With Tunable Networks
Impedance-matching networks must be tunable before they can be used over a wider frequency range or match a wider range of impedances for lower standing wave ratio (SWR) values. One or more of the components must be variable to make such networks. While manually variable capacitors and inductors are available, they are too large for practical modern circuits and their variability cannot controlled electronically. Electronic control permits automatic tuning and matching circuits to be built.
Different types of electronically variable capacitors are now available to implement such automatic tuners and matching circuits. The varactor diode or voltage variable capacitor has been available for years, and its continuously variable nature over a wide capacitance range is desirable. However, it is nonlinear and requires a significantly high bias voltage for control. Two other available options are the digitally tunable capacitor and the microelectromechanical-systems (MEMS) switched capacitor. Both are available in IC form and are ideal for making high-frequency variable matching networks.
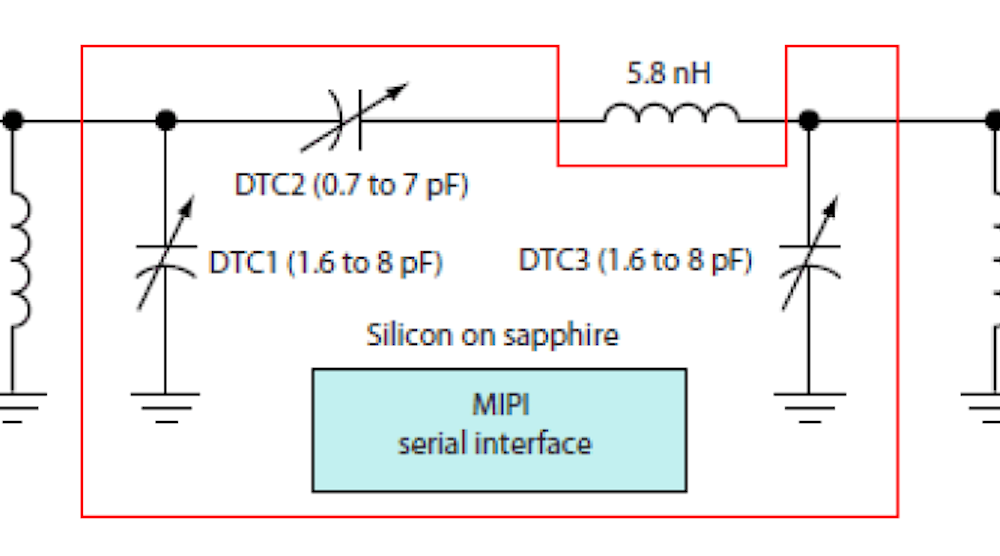
Peregrine Semiconductor’s PE64904 and PE64905 Digitally Tunable Capacitors (DTCs) consist of five fixed capacitors switched by an array of MOSFET switches(Fig. 4)。These devices are made using a unique silicon-on-sapphire process. The capacitance is changed by a serial 5-bit code word using either a serial peripheral interface (SPI) or an I2C interface. The capacitor may be used in a series or parallel format. Maximum shunt capacitance is 5.1 pF with a minimum of 1.1 pF. Maximum series capacitance is 4.6 pF with a minimum of 0.6 pF. The capacitors can be put in series or parallel for larger or smaller values.
Figure 5shows a circuit using several of these capacitors. It’s both a tunable filter and impedance-matching circuit. It’s also a reconfigurable coupled resonator topology that’s widely used in band-pass filters and impedance-matching networks. Using external inductors, this network provides wide impedance coverage over the cellular phone bands of 698 to 960 MHz and 1710 to 2170 MHz. Such tunable networks can provide automatic adjustment when cell sites are changed or can correct for the antenna detuning when the phone is held.
Wispry’s MEMS devices also are commercially available tunable capacitors. The basic element is a MEMS capacitor that can be switched to produce an incremental change of 0.125 pF per bit. Each capacitor comprises a fixed plate with a dielectric on its surface. Above it is a mechanical flap forming the other plate. When an electrostatic charge is applied to the plates, they’re attracted to one another. The upper plate is pulled downward, significantly decreasing plate spacing and increasing capacitance. By forming an array of these tiny capacitors, larger values can be created.
The company makes several versions of this device including custom circuits. Capacitance values to a maximum of 10, 20, or 30 pF can be formed with a tuning range of 10:1. The capacitance is controlled digitally with a serial word using either an SPI or the MIPI radio-frequency front-end (RFFE) interface. Capacitive devices use external inductors.
Also, WiSpry’s WS2017 standard impedance matching network is a variable p-network matching device featuring on-chip inductors. Again, the primary application is automatic tuning and impedance matching in cell phones and other small RF equipment. It operates over the 824- to 2170-MHz frequency range. An on-chip dc-dc converter provides the high voltage to operate the switchable capacitors. The device uses an SPI for control. A similar product, the WS2018, has similar specifications as well as the MIPI RFFE interface.
References
- Bostic, Chris,RF Circuit Design, Howard W. Sams, 1982.
- Frenzel, Louis E.,Principles of Electronic Communication Systems, McGraw Hill, 2008.
>> Electronic Design Resources
。。>> Library: Article Series
。。.. >> Series: Impedance Matching