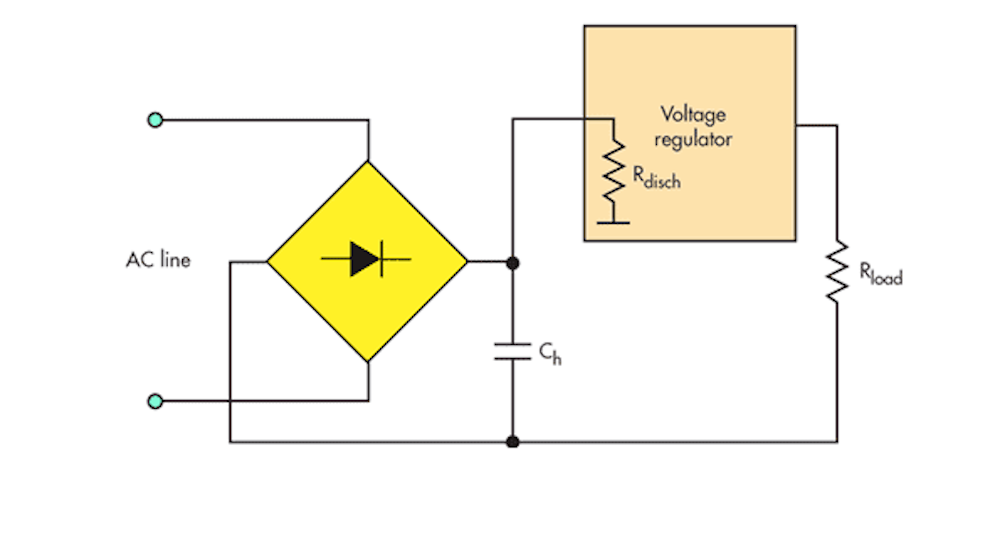
许多电源使用固定电容器在全波或桥梁整流器输出处保持足够的能量,以便当整流电压下降并在交流电源电压的下半循环时再次上升时,以供应负载。当整流线电压在固定电容器上的电压以下时,电容器会供电后的电动转换器电路。结果,该电容器可确保整个电源的平滑,无抛弃操作。
The hold-up capacitor is charged from the rectifier output, through the very low resistance of the rectifier and ac line, so the voltage across the capacitor follows the rectified line voltage as it charges(Fig. 1)。然后,电容器通过提供负载的电源转换器排放。与线性相比,当固定电容器提供开关调节器时,其所需值有很大差异,因此我们将分别查看它们。
切换调节器电源
We can neglect power loss in a switching regulator due to its high efficiency.
describes the hold-up capacitor voltage while charging. (The absolute-value sign is used to describe the rectifier action.) V在_maxis the peak value of the rectified voltage. The hold-up capacitor voltage, while discharging, is defined by:
where P在is the converter’s input average power, and VC是目前的电容器电压。使用这些参数,等效放电性rdisch可以用来确定Ch, the hold-up capacitance. Note that VC本质上等于VHoldUp(t) here.
These charge and discharge curves meet up in another cycle, at time t0:
通过取消V在_max, 我们获得:
要获得平均电压V的值C_AVof the hold-up capacitor, define rdischusing:
Note that the VCchanges while Chdischarges, with the same changes as rdisch。To simplify the analysis, we have to find out the average value for the discharge resistance. VC从V成倍更改在_maxthrough Vdisch。我们知道V的值在_max和vdisch, and assuming the discharge process is linear, we can find the voltage across average value of Chusing:
该电压值可用于计算排放过程常数:
表达:
表示固定电容器放电时间常数。
Solving Equation 4 with respect to Ch, 我们获得:
这是关于t的先验方程0and is very hard to solve symbolically, although it would be very interesting to use it to obtain the value for t0directly and then figure out how the “meeting point” t0depends on the capacitance of the hold-up capacitor.
Instead, solve the equation with respect to Ch。When Ch放电,这样做,直到达到预定的阈值电压Vdisch对于时间间隔t0using:
哪个导致:
Substituting Equation 7 into Equation 5, we obtain:
from which we get:
该公式表明提供V的排放电压disch在某个负载值和线频率ω处,固定电容器应具有C的值h。
示例1
With a line voltage V线= 415 V, load power Pload= 70 W, and efficiency η =97.2%,然后:
V在_max= √2 × V线= 587 V
Assign:
Vdisch=√2/2×V在_max= 415 V时F = 50 Hz,ω=2πf= 314秒-1, and P在= pload/η= 72 w
From this we obtain a value for VC_AV:
which leads to a value for the hold-up capacitor:
with Ch= 6.21 × 10-6F,对于固定电容器来说,这是一个相当高的价值。
We can plot a graph for this example(图2)。
As discharge-margin Vdischis lowered, more energy should be supplied to the hold-up capacitor to fully charge it, as seen from:
At this point, the hold-up capacitor starts to charge, as indicated by:
我们可以从能量平衡的角度来计算持有电容值:
这显示了在电容器放电时应供应负载的固定电容器中存储的能量量,以及放电电压和固定电容器值。
线性调节器供应
The situation for a linear regulator is very different than for a switching regulator. With Vloadas the voltage across the load, and Ploadas the power to the load, we clearly have:
The linear regulator resistance is given by:
[等式21]
The time constant is given by:
将其替换为等式4的收率:
并解决Chwe get:
When Chdischarges, we find Vdisch来自:
which leads to t0:
将等式26替换为等式24以获得:
然后解决Ch通过:
示例2
使用pload= 70 W和Vload= vdisch- 2.5 V.然后确定Ch通过:
如果示意图具有线性调节器,则固定电容器将具有更高的值,因为它应该存储足够的能量以在整个线性调节器上提供功率损失。