你会学到什么:
- 11 essentials to focus on when trying to increase data-rate speeds.
- 处理带宽约束。
- 调制和MIMO方法。
What’s the one dominating factor driving virtually all electronic new product design today? To some it might be low power consumption, but it’s not too difficult to identify higher speeds and faster data rates as the main objective guiding most new ICs, equipment, systems, and technology development.
年复一年year, all electronic devices just keep getting faster. Memory speed, processor speed, Wi-Fi, and other communications data rates continue to rise. Tom Cruise’s character Maverick in the popular 1980s movie壮志凌云stated in this blog’s headline what we all feel about electronics today.
We like higher speeds because we hate to wait. In our instant gratification society, we want split-second video downloads, lower-latency everything, and no waiting for whatever the application. The whole industry has responded with a continuous stream of faster products. And that speed quest continues.
How do we make data go faster? Just out of curiosity as an intellectual exercise, I’ve summarized the factors that I could think of to achieve higher communications data rates, for whatever it’s worth:
1.Bandwidth and the communications medium.可用的有线和无线媒体决定了您可以走的速度。对于电线数据传输,我们使用改变类型的介质,如双绞线,同轴电缆和光纤电缆。所有这些都具有确定可用于快速数据的带宽的上频率限制。
对于无线,载波频率最终确定最大可能的数据速率。同样,可用带宽设置上限。随着数据速率上升,需要更多带宽,这意味着推动更高的频率以使其发生。但是,我们受FCC或其他机构施加的规定限制。此外,必须使用电子元件来实现所需的更高频率。底线,带宽是实现高速的主要决定因素。
2.Constrained by physics.The Shannon-Hartley law states the relationship between bandwidth and data rate:
C = 2B
这里C是信道容量或串行数据率in bits per second and B is the bandwidth in hertz. It says that with a bandwidth of 3,000 Hz, you can have a maximum data rate of 2(3,000) = 6,000 bits per second. Data rate C is determined by the bit time (t) in a serial data stream or C = 1/t. Of course, this is all theoretical and assumes a perfect medium and no noise. If noise is present, the data rate will be even less.
3.The effect of noise.Here’s the complete Shannon-Hartley law:
C = B日志2(1 + S/N)
信号和噪声(n)值以功率给出。信噪比(SNR)清楚地影响数据速率。噪声水平越大,给定带宽可能发生的最大数据速率越大。
4.Boosting data rate in a fixed bandwidth.通过窄频道获得每秒的更多位的流行方式是使用将位转换为符号的编码类型。符号是使用多电压电平,多个相移,多个频率偏移的信号,或类似方案的组合来表示相同符号间隔内的两个或更多个比特。应用这些方案时,可以在较窄的带宽中实现更高的数据速率:
C = 2B日志2N
where N is the number of symbol levels used. Examples include:
- 8PAM uses eight voltage levels, with each level representing three bits—000 through 111—for a data rate that’s 3X the symbol rate.
- 4FSK利用四种不同的频率,每个频率表示两个位。对于所使用的每个频率,传输两位,数据速率加倍。
5。Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).数据链路的可行性或其效率由误码率(BER)确定。BER是一秒钟内发生的位错误的数量。对于一个很好的频道,BER低于或优于10-5to 10-11。随着数据速率的增加,比特错误数量增加。这是因为比特电压将通过噪声修改而转换,这使得比特更难识别。然后减少数据速率,随着比噪声转换更高的能量,对BER比特时间变得更长的效果。
6。Forward error correction (FEC).Several methods of detecting and correcting errors on-the-fly have been developed. Adding extra bits to the data stream enables bit errors to be identified and corrected. These methods are either hardware, software, or a combination of the two. The end effect is as if there was an increase in transmit power, thereby permitting higher data rates.
This outcome is referred to as coding gain. For instance, using FEC can produce results equivalent to increasing signal power by 3 db. A 3-dB increase is equivalent to doubling transmit power. As a result, lower BER allows for an increased data rate. The downside is that adding extra bits to the data stream lowers throughput.
7。Spectral efficiency.The way we measure and express how much speed we can get through a given bandwidth is spectral efficiency given in bits per second per Hz. If we measure 780 Mb/s through a 40-MHz channel, the spectral efficiency is 780/40 = 19.5 b/s/Hz.
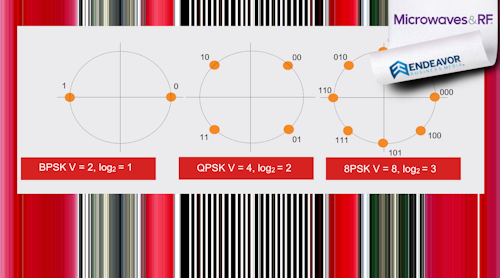
8.调制。调制方法也可以产生更高的速度。您听说过包含QAM和OFDM的示例。正交幅度调制(QAM)采用幅度和相移的组合来产生增加数据速率的符号。64QAM使用64个符号来定义6位代码。发送一个符号产生6位流,从而将基本符号率乘以6并导致6倍数据速率增加。
正交频分复用(OFDM)在分配的带宽中使用多个子载波。要传输的数据被划分为多个较低速度的流,每个流是每个调制子载波的数据。使用数百或数千个子载波将较低的数据速率乘以极高的数据速率。
9.Multiple input, multiple output (MIMO).MIMO takes advantage of multiple transmitters (TX), receivers (RX), and antennas. The data to be transmitted is divided into multiple lower-rate streams and each is transmitted over the same bandwidth to multiple receivers. This process multiplies the data rate by the number antennas and TX/RX paths. A typical arrangement is 4×4 or four TX and four RX.
At higher frequencies, the smaller antennas permit dozens or hundreds to multiple data paths that boost data rate. Add in agile beamforming using phased arrays in the GHz bands that boost power levels, and you can increase data rates even further.
10.Compression.我开始向此列表添加数据压缩,但数据传输中的不常见。数据压缩主要用于减少像视频一样的大规模数据的存储要求。然而,在某些类型的通信中,较短的消息转化为更高的数据吞吐量。
11.组合。在实践中,将上述几种方法组合以实现显着的数据速率。较新版本的Wi-Fi和5G蜂窝使用大多数上述技术以提供高于1 GB / s的数据速率。
我想知道的是,我们将来会在未来看到哪些新技术,以创造更高的速度?我们几乎达到了技术的极限吗?或者我们可以很快看到Terabit速度?